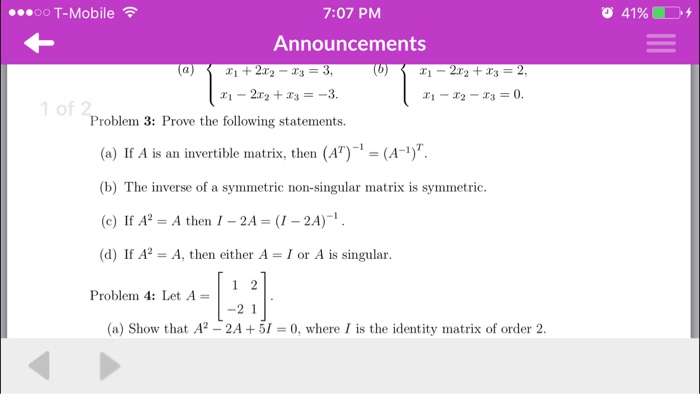
Invertible Symmetric Matrix Proof
A negative definite Hermitian symmetric matrix must have all strictly neg-ative eigenvalues. BACD BAC gives BI D IC or B D C.
Here we assume the dimensionalities of these blocks are.

Invertible symmetric matrix proof. The function finverts all non-zero numbers and maps 0 to 0. Recall that a symmetric matrix is positive-definite if and only if its eigenvalues are all positive. Any power A n of a symmetric matrix A n is any positive integer is a symmetric matrix.
Thus AB T A T B T. But A and B are symmetric. The determinant is the product of the eigenvalues.
For a positive integer n consider the tridiagonal matrix of order n M 2 6 6 6 6 4 1 1 1 2 1. Eigendecomposition when the matrix is symmetric. This means AB T AB.
But a block diagonal matrix is positive denite ieach diagonal block ispositive denite which concludes the proof. A sufficient condition for a symmetric n n matrix C to be invertible is that the matrix is positive definite ie. 1 2 1 1 1 1 n 3 7 7 7 7 5.
Invert the part of the matrix that is invertible its image and to leave alone the part of the matrix that is not invertible its kernel. And we know that for any symmetric matrixT and any invertible matrixN the matrix is positive denite T0 iN T Nwhich is obviously symmetric is positive denite N T N0. 1 Let A and B be symmetric matrices of the same size.
A Prove that A is invertible. Spectrum of the matrix. A If A is invertible then A 1 is itself invertible and A 1 1 A.
Suppose that the matrix A is diagonalizable by an orthogonal matrix Q. 52 Quadratic Forms A motivating quote from David Lays Third Ed Linear Algebra and Its Applica. A symmetric matrix is positive-definite if and only if its eigenvalues are all positive.
The decomposed matrix with eigenvectors are now orthogonal matrix. We need to prove that AB is symmetric. The inverse of a symmetric matrix happens to be the same as the inverse of any matrix.
Fx 1x x6 0 0 x 0. Thus since A is positive-definite the matrix does not have 0 as an eigenvalue. Show that if A is diagonalizable by an orthogonal matrix then A is a symmetric matrix.
Then we can conjugate to get Ax λx. Diagonalizable by an Orthogonal Matrix Implies a Symmetric Matrix Let A be an ntimes n matrix with real number entries. In mechanics its called the principal axis theorem.
Theorem Properties of matrix inverse. The inverse matrix can also be divided into four blocks. This proves that complex eigenvalues of real.
From 11 we have µi 2µi1 µi2 for i 2n 1 and µn 1 1 n µn1 µn2 with initial conditions µ0 1 and µ1 1. Then B D C according to this proof by parentheses. The orthogonality of the.
And are and are and are. Suppose A is symmetric and Ax λx. So if we apply fto a symmetric matrix.
We can do this by applying the real-valued function. The transpose of a sum is the sum of transposes. Since others have already shown that not all symmetric matrices are invertible I will add when a symmetric matrix is invertible.
Note 3 If A is invertible the one and only solution to Ax D b. A symmetric matrix is invertible if and only if none of its eigenvalues which are all real numbers is the zero eigenvalue. The answer thus is.
A square matrix is invertible if and only if its determinant is not zero. Therefore you could simply replace the inverse of the orthogonal matrix to a. Some symmetric matrices are invertible and others are not.
Recall a property of transposes. A symmetric Hermitian indefinte matrix is one that has some positive and some negative and possibly zero eigenvalues. As such any matrix whose multiplication takes place from the right or the left with the matrix in question results in the production of the identity matrix.
We can use this observation to prove that A T A is invertible because from the fact that the n columns of A are linear independent we can prove that A T A is not only symmetric but also positive definite. So AB T AB and the proof. B If A is invertible and c 0 is a scalar then cA is invertible and.
2 This shows that a left-inverse B multiplying from the left and a right-inverse C multi-plying A from the right to give AC D I must be the same matrix. In addition any matrix of the form QΛQT will be symmetric. If A is an invertible symmetric matrix then A-1 is also symmetric.
So it too is invertible. Theorem 2inverse of a partitioned symmetric matrix Divide an symmetric matrix into four blocks. 41 Then M is invertible and the inverse is M1 maxfijg ij1n.
Thus A T A and B T B. Real eigenvalues Why are the eigenvalues of a symmetric matrix real. X R n 0 x T C x 0.
If the entries of A are real this becomes Ax λx.

For Any N X N Matrices A And B Prove That A Aa Is Chegg Com
Solved Prove The Following Statements If A Is An Inverti Chegg Com

2 A I Give The Definition Of N N Symmetric Matrix Chegg Com
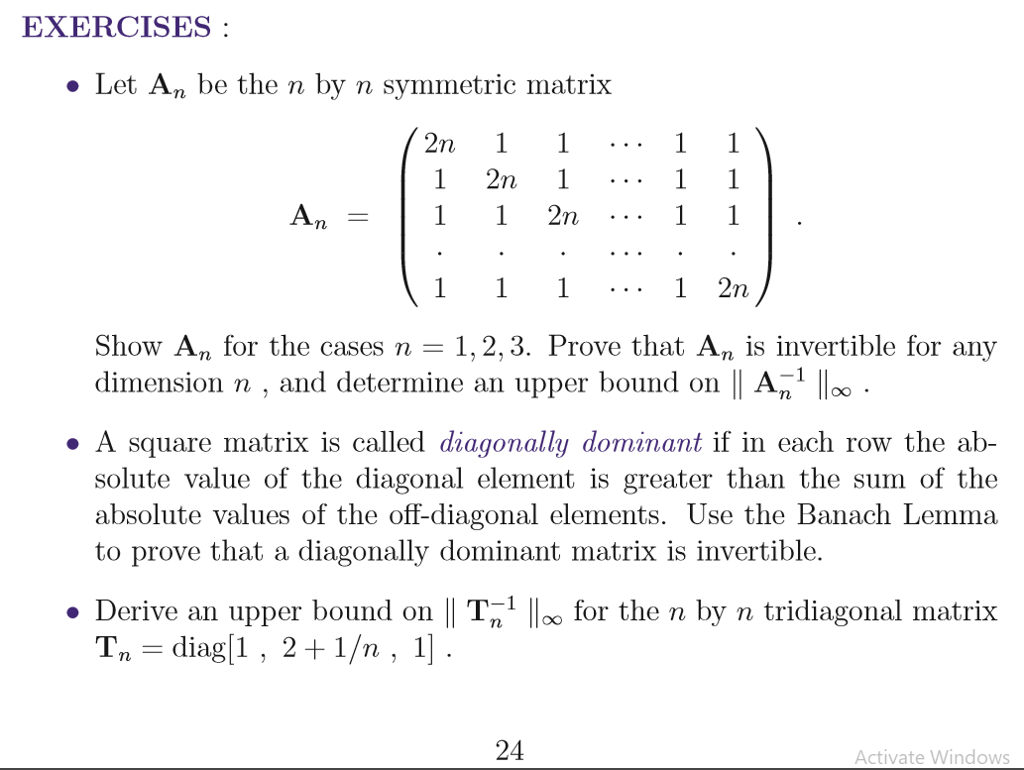
Exercises Let An Be The N By N Symmetric Matrix 1 Chegg Com

Matrix Inverse Properties Youtube

Prove That If A Is Nonsingular Matrix And Ab 0 Then B Is Null Matrix Proof Youtube

Example Proving That The Left Inverse Of A Matrix Is The Same As The Right Inverse Youtube

Proof If N Is Odd Then Det A 0 For Skew Symmetric Matrix Youtube

Proof For Why Symmetric Matrices Are Only Orthogonally Diagonalizable Mathematics Stack Exchange

Linear Algebra 90 Symmetric Matrices Proofs Youtube

Proof For Why Symmetric Matrices Are Only Orthogonally Diagonalizable Mathematics Stack Exchange

Proof If N Is Odd Then Det A 0 For Skew Symmetric Matrix Youtube

The Inverse Of An Invertible Symmetric Matrix Is A Symmetric Matrix Youtube
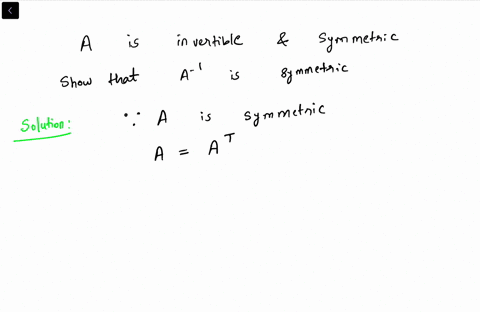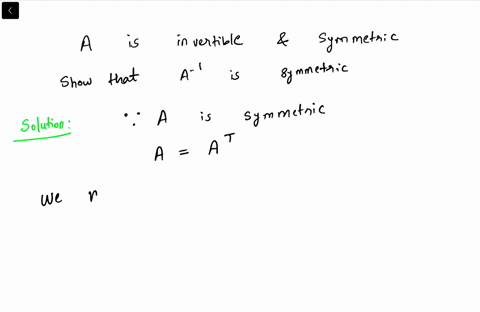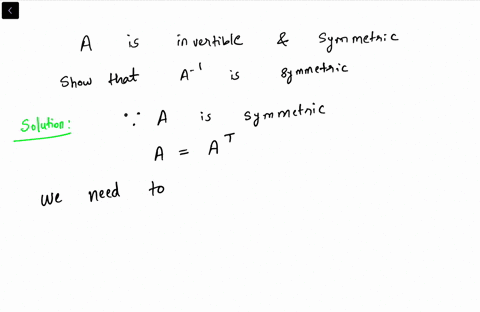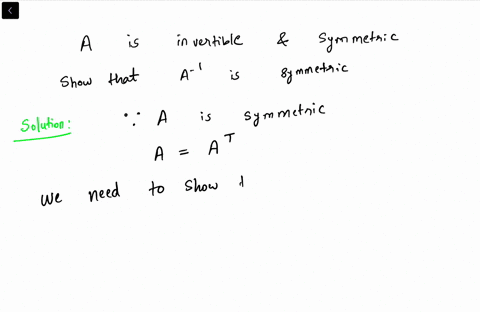
Solved Use Properties Of The Inverse To Prove The