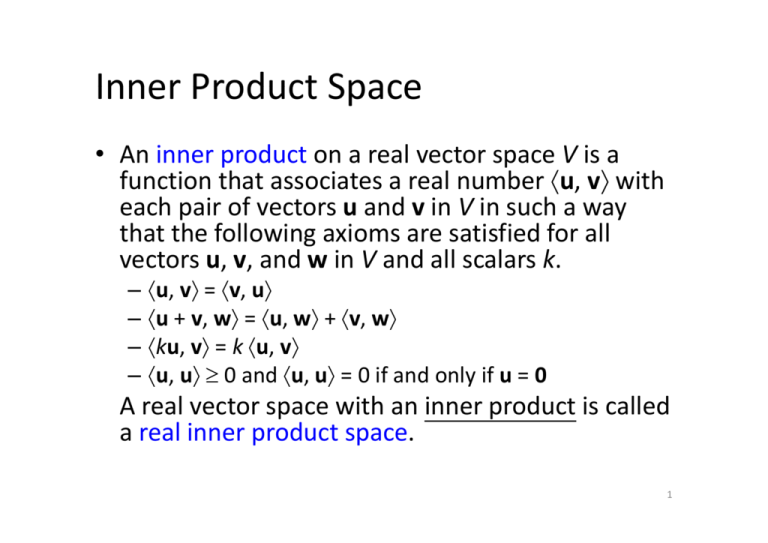
Inner Product Orthogonal Matrix Proof
Two vectors uv 2Rn are orthogonal if uv 0. For example kxk2 xx UxUx kUxk2 so kxk kUxk.

Inner Product Spaces Linear Algebra Notes
I know that if v w are orthogonal they are linearly independent.

Inner product orthogonal matrix proof. Since U preserves inner products it also preserves lengths of vectors and the angles between them. 1 Real inner products Let v v 1v n and w w 1w n 2Rn. For any vectors uv in an inner product space V huvi2 huuihvvi.
5 Cauchy-Schwarz inequality Theorem 51 Cauchy-Schwarz Inequality. Which is multiplying the length of the first vector with the length of the second vector with the cosine of the angle between the two vectors. TrZ is the trace of a real square matrix Z ie TrZ P i Z ii.
Let AB be matrices of the inner product relative to bases BB0 of V respectively. On Wolframs website but havent seen any proof online as to why this is true. So the distances from to or from to should be identical if they are orthogonal perpendicular to each other.
This is a pretty simple proof. The the orthogonal complement of S is the set S v V hvsi 0 for all s S. Yet there is also a geometric definition of the dot product.
V k 0 and w 1. A UxUy UyUx yUUx yIx yx xy. This well-known theorem has numerous different proofs.
That means that the projection of one vector onto the other collapses to a point. Now if I suppose v 1. So if x y e i then AxAy Ae iAe i v iv i.
The product of two unitary matrices is unitary. Two vectors are orthogonal if and only if kuvk2 kuk2kvk2. Note that the convention in physics is.
This well-known theorem has numerous different proofs. A b a b cosø. Thus you can think of the wordorthogonal as.
Inner Product on a Real Vector Space. Lets start with v v1v2vn v v 1 v 2 v n and compute the dot product. Similarly uav avu a vu a vu a uv.
So the claim is false for orthogonal columns. A If A is positive definite then x y x T A y defines an inner product. We have the following properties for the inner product.
Prove that v w 2 v 2 w 2 iff v w are orthogonal. D Smaps an orthonormal basis to an orthonormal basis. 4 SYMMETRIC MATRICES AND INNER PRODUCTS the way matrix multiplication is carried out.
Ax xˇ1xˇ2xˇn A hasexactlyoneelementequalto1ineachrowandeachcolumn Orthogonalitypermutationmatricesareorthogonal ATA I becauseA hasexactlyoneelementequaltooneineachrow ATAij Xn k1 AkiAkj ˆ 1 i j 0 otherwise. The notion of inner product allows us to introduce the notion of orthogonality together with a rich family of properties in linear algebra. The following are equivalent.
Two vectors are orthogonal if and only if kuvk2 kuk2kvk2. When we substitute ø with 90 cos 900 ab becomes zero. B For all uv2V hSuSvi huvi.
If P is the transition matrix from B to B0. Let S be a subspace of the inner product space V. On the other hand x y e ie i 1.
De ne the length or norm of vby the formula kvk p hvvi q v2 1 v2n. Then QS SQ S1Q1 QS1 so QS is unitary Theorem 3. Aij 0 if j ˇi Ax isapermutationoftheelementsofx.
2 If S is a subspace of the inner product space V then S is also a subspace of V. The algebraic definition. The notion of inner product allows us to introduce the notion of orthogonality together with a rich family of properties in linear algebra.
B If x y x T A y defines an inner product then A is symmetric positive definite. Here Rm nis the space of real m nmatrices. Schur Lemma If A is any square complex matrix then there is an upper triangular complex matrix U and a unitary matrix S so that A SUS SUS1.
Inner product space is said to be an isometry if satis es jjSvjj jjvjjfor each v2V. But v iv i will not be equal to one unless v i is a unit vector. Ive seen the statement The matrix product of two orthogonal matrices is another orthogonal matrix.
V V is an isometry. Let V be a flnite-dimensional inner product space. Expanding the equation jjS u vjj2 jj u vjj2.
Suppose Q and S are unitary so Q 1 Q and S S. Assume that S is an isometry. For the additivity note that uvw vwu vu wu vu wu uv uw.
The matrix inner product is the same as our original inner product. Two vectors are orthogonal to each other if their inner product is zero. Weassociatewithˇthen n permutation matrix A Aiˇi 1.
Two vectors uv 2Rn are orthogonal if uv 0. Orthogonal Inner Product Proof. W k 0.
And the angle between the two perpendicular vectors is 90. Let v and w be elements of an inner product space. The standard inner product between matrices is hXYi TrXTY X i X j X ijY ij where XY 2Rm n.
We de ne the inner product or dot product or scalar product of v and w by the following formula. Then B PTAP. C The columns of a unitary matrix form an orthonormal set.
V v v1v2vn v1v2vn v2 1 v2 2v2 n 0 v v v 1 v 2 v n v 1 v 2 v n v 1 2 v 2 2 v n 2 0. Thus two vectors inR2are orthogonal with respect to theusual Euclidean inner product if and only if the cosine of the angle betweenthem is0 which happens if and only if the vectors are perpendicular in theusual sense of plane geometry. Note that we can de ne hvwifor the vector space kn where kis any eld but kvkonly makes sense for k R.
However if the columns form an orthonormal basis. Hvwi v 1w 1 v nw n. 1 If U and V are subspaces of a vector space W with U V 0 then U V is also a subspace of W.
The inner product is anti-linear in the second slot that is uvw uv uw for all uvw V and uav a uv. Whereis the angle betweenuandvthinking ofuandvas arrows with initialpoint at the origin.

The Equation Of A Plane Mp4 Plane Math Equation Of Plane High School Math

Why Does The Fact That Tv Is Orthogonal To V For All V Implies T Is The Zero Operator Break Down For Real Inner Product Spaces Mathematics Stack Exchange

Cross Product Introduction Formula Vectors Video Khan Academy

Effect Of Applying Various 2d Affine Transformation Matrices On A Unit Square Note That The Reflection Mat Matrices Math Studying Math Physics And Mathematics

Linear Algebra Inner Product Space Gram Schmidt Orthogonal Complement Mat223 Past Test Youtube

Part 23 Orthonormal Vectors Orthogonal Matrices And Hadamard Matrix By Avnish Linear Algebra Medium

How Can An Inner Product Be Defined Through A Proof Mathematics Stack Exchange

Part 23 Orthonormal Vectors Orthogonal Matrices And Hadamard Matrix By Avnish Linear Algebra Medium
Orthogonal Matrices Linear Algebra
Https Math Berkeley Edu Mcivor Math54s11 Worksheet3 11soln Pdf

Proving Qv Cdot Qw V Cdot W Given Q Is Orthogonal Mathematics Stack Exchange

Need Help With This Lab I Need To Solve Problem 1 2 Chegg Com

If The Inner Product Of Two Matrices Is Zero What Does That Mean
Https Users Math Msu Edu Users Parker 309 Exam3 Solutions Pdf
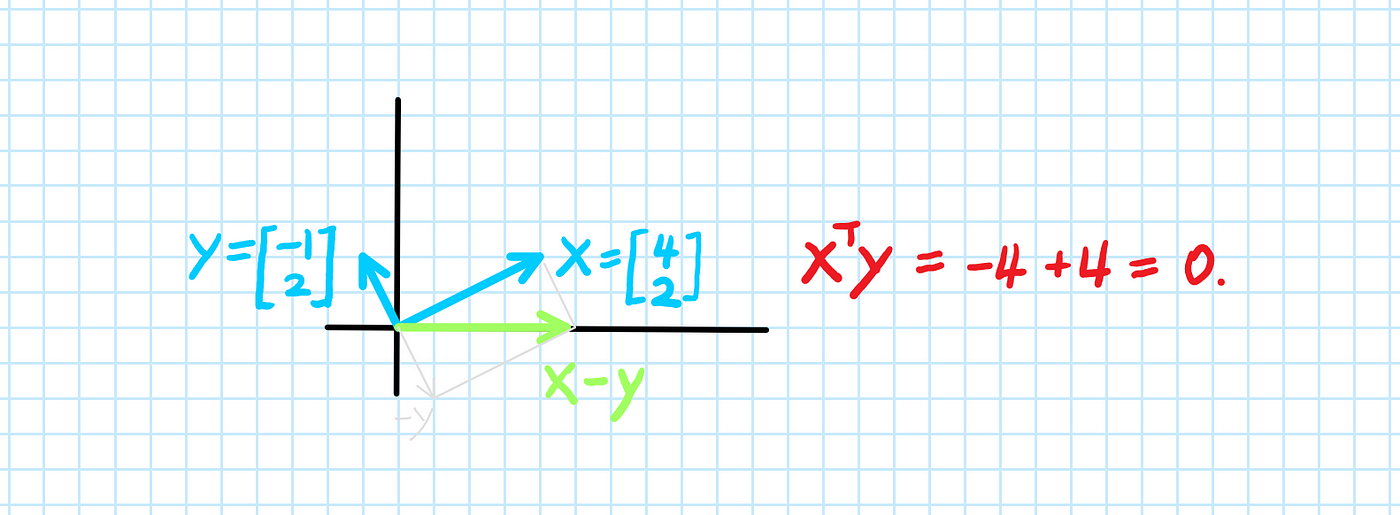
Why Is The Dot Product Of Orthogonal Vectors Zero By Aerin Kim Towards Data Science
Https People Math Umass Edu Havens M235lectures Innerprods Pdf