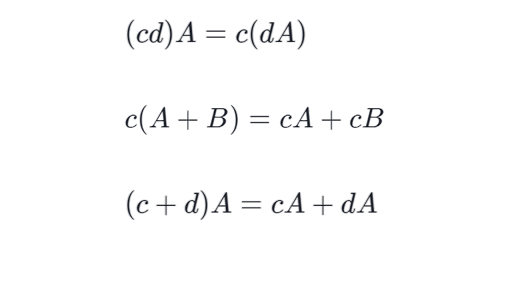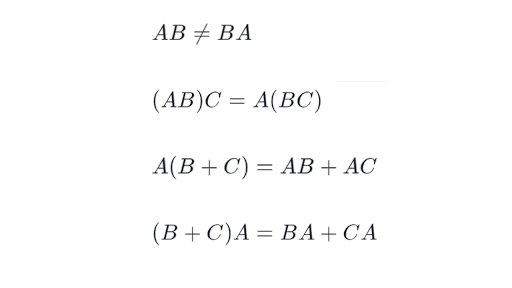Matrix Multiplication Rules Distributive
The entries in matrix C are obtained as follows. From the above two examples we can observe the following for the matrix multiplication AB C.

Properties Of Matrix Multiplication Proof
TheoremProperties of matrix inverse.
Matrix multiplication rules distributive. Two matrices can only be multiplied if the number of columns of the matrix on the left is the same as the number of rows of the matrix on the right. Also if A be an m n matrix and B and C be n m matrices then. Again by applying the definition of Kronecker product and that of multiplication of a matrix by a scalar we obtain Zero matrices.
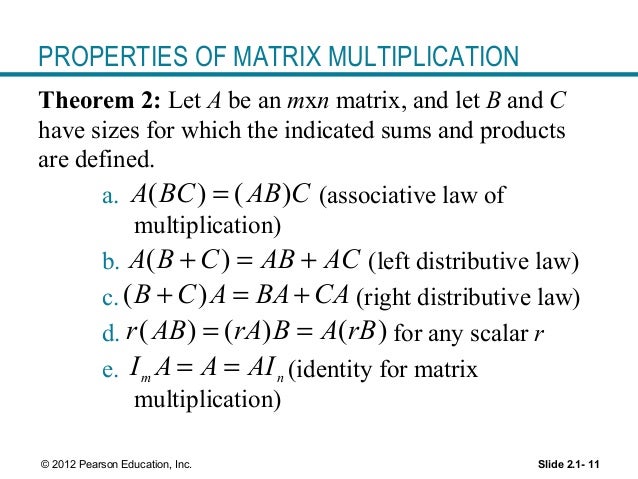
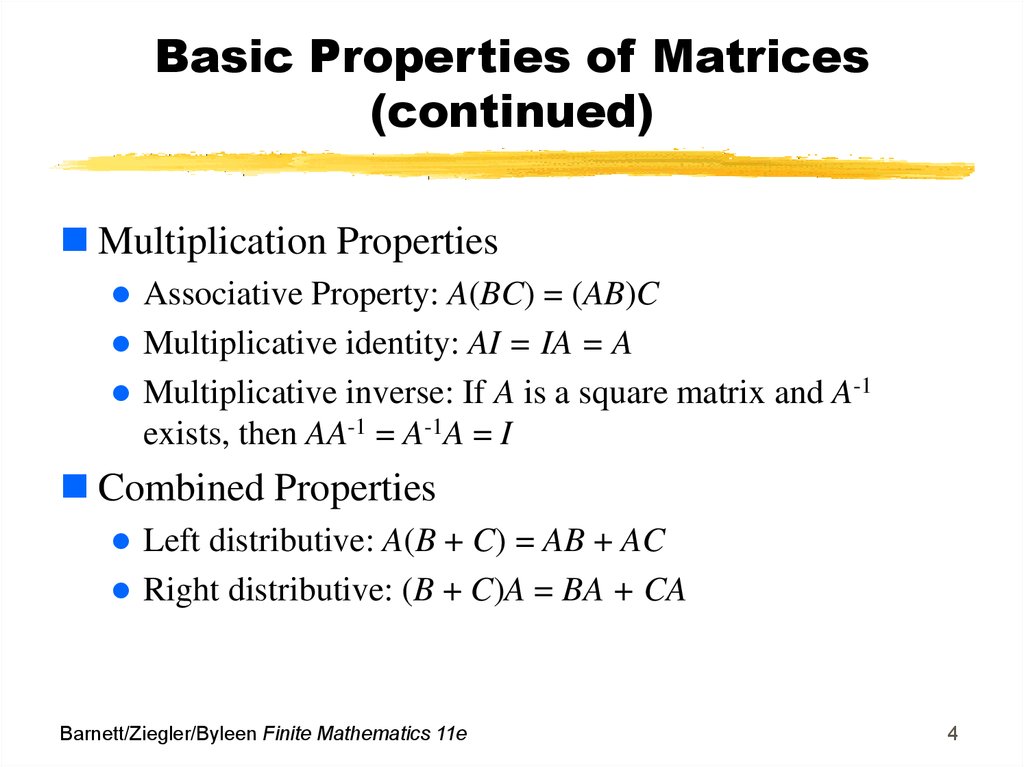
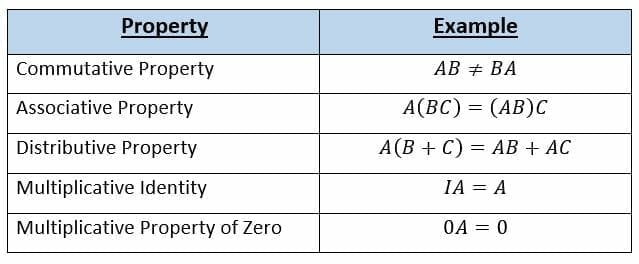
A B C AB AC A B C AC BC 5. For every square matrix A there exists an identity matrix of the same order such that IA AI A. The inverse of a matrixAis uniqueand we denote itA1.
B CA BA CA. A b a T b displaystyle left mathbf a cdot mathbf b rightmathbf a operatorname T mathbf b. A more general rule regarding the multiplication by scalars and follows.
Matrix C has the same number of rows as matrix A and the same number of columns as matrix B. If Ais invertible andc 0is a scalar thencAis invertible andcA11cA1. In this proof Im assuming that the matrix of the composition is the product of the matrices Matrix multiplication is defined so that this is true Im also assuming that the matrix of the sum is the sum of the matrices.
Matrix multiplication is distributive over matrix addition. L A L B L C L A L B L A L C. Then find B CA and BA CA.
However we have the following identifications which respect the linear structure. You are right that formally speaking we cannot multiply a 1 1 matrix with a matrix of any size. A BC AC BC cAB cAB AcB where c is a constant please notice that AB BA Multiplicative Identity.
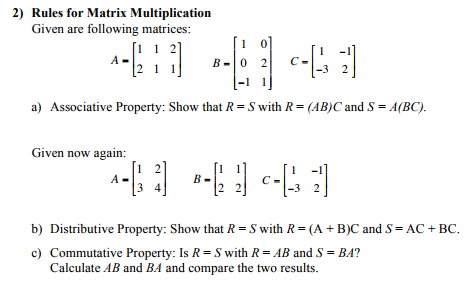
Clearly any Kronecker product that involves a zero matrix ie a matrix whose entries are all. The Distributive Property of Matrices states. A 1 2 0 1 B 0 1 1 1 C 2 0 0 1.
Scalars 1 1 matrices Scalar matrices of any size. If C has size m n you can view λ as the m m scalar matrix. Matrix multiplication is distributive over matrix addition.
AB C AB AC Distributive. The dot product of two column vectors a and b can be computed as the single entry of the matrix product. If Ais invertible thenA1is itself invertible andA11A.
The determinant of a square matrix is the same as the determinant of its transpose. The distributive property holds. Due to the matrix multiplication rules not all matrices can be multiplied.
Find AB C and AB AC. Since A and B satisfy the rule for matrix multiplication the product AB can be found as follows. Thus under this identification it makes sense to multiply any matrix C by a scalar λ.
AB C AB AC. Matrix AB is a 2 x 2 matrix. It follows that A B C A B A C.

Properties Of Multiplication Of Matrices With Proof Teachoo
Given Are Following Matrices A 1 1 2 2 1 1 B Chegg Com

Matrix Algebra Lecture Part 4 Laws Of Matrix Algebra Youtube
Matrix Equations And Systems Of Linear Equations Online Presentation

Distributive Law Of Multiplication Over Addition For Matrices Math Lecture Sabaq Pk Youtube

Linear Algebra 59 Matrix Multiplication Properties And Proof Of Scalar Multiplication Youtube

Multiply Matrices Use The Properties Of Matrix Multiplication Ppt Download

Properties Of Multiplication Of Matrices With Proof Teachoo
Matrix Multiplication Explanation Examples

Chapter 2 Matrices 2 1 Operations With Matrices

3 4a Matrix Operations Finite Math

Section 1 4 Inverses Rules Of Matrix Arithmetic Ppt Download
Properties Of Matrix Scalar Multiplication Article Khan Academy

Section 1 4 Inverses Rules Of Matrix Arithmetic Ppt Download
Properties Of Matrix Multiplication Article Khan Academy

2 1 Operations With Matrices 2 2 Properties Of Matrix Operations Ppt Video Online Download

Associative Property Of Matrix Multiplication Video Khan Academy

Lecture 4 Chapter 1 Review Section 2 1

Linear Algebra 58 Matrix Multiplication Properties And Proof Of Distributative Law Youtube